The origins of the metal building history date back nearly
100 years. Early in the 20th century, steel products companies began to appear.
Their products were generally agricultural – water troughs, feed bins, grain
bins, etc. These were mass-produced and traditionally of a single size.
Therefore, they could be “pre-fabricated” – a ready inventory to be delivered
when the customer needed it.
As time progressed, rudimentary building designs
began to emerge, such as the pre-fabricated garage. Again, this was a limited
product offering dimensionally, which allowed the garage to be carried in an
inventory.
During World War II, a need arose for structures
such as barracks and maintenance facilities that could be containerized and
shipped – ready to erect. This was a perfect outlet for steel products
companies. Buildings were produced that required no welding. They were
bolted-up, lending themselves to simple, quick construction as the war advances
and occupations unfolded.
By the end of the war, it was clear that the
industry would not return to its pre-war product offerings. Metal buildings
were here to stay. The post-war construction boom offered an ideal opportunity
to mass produce buildings for a variety of non-residential industries. Metal
building companies learned that partnerships with local contractors across a
region or even the entire country were an effective way to deliver an erected
building structure to the end customer.
Buildings during this time were still pre-fabricated
as the marketplace adapted to the limited, set sizes that were available.
However, structural engineers began to design more and more standard-size
offerings to meet demand and soon pre-fabrication was no longer possible. At
this time, still well before the computer age, the process came to be known as
the “pre-engineered” metal buildings industry.
This configuration continued from the 1950s on into
the mid-1980s. The advent of the computer to analyze and design structural
members quickly has ultimately led to the modern make-to-order process that
exists today. The pre-engineered system previously known is now limited to roof
and wall panels and some connections design.
Today,
the metal building industry boasts a capability of producing buildings for
virtually any low-rise, non-residential end use. These building designs are
performed quickly by industry engineers, who have vast knowledge of the
building codes utilized in the United States. The custom design practice allows
for economy in building design that makes metal buildings very attractive to
the marketplace.
PEB –
Features & Advantages
Features and
Advantages
Features:
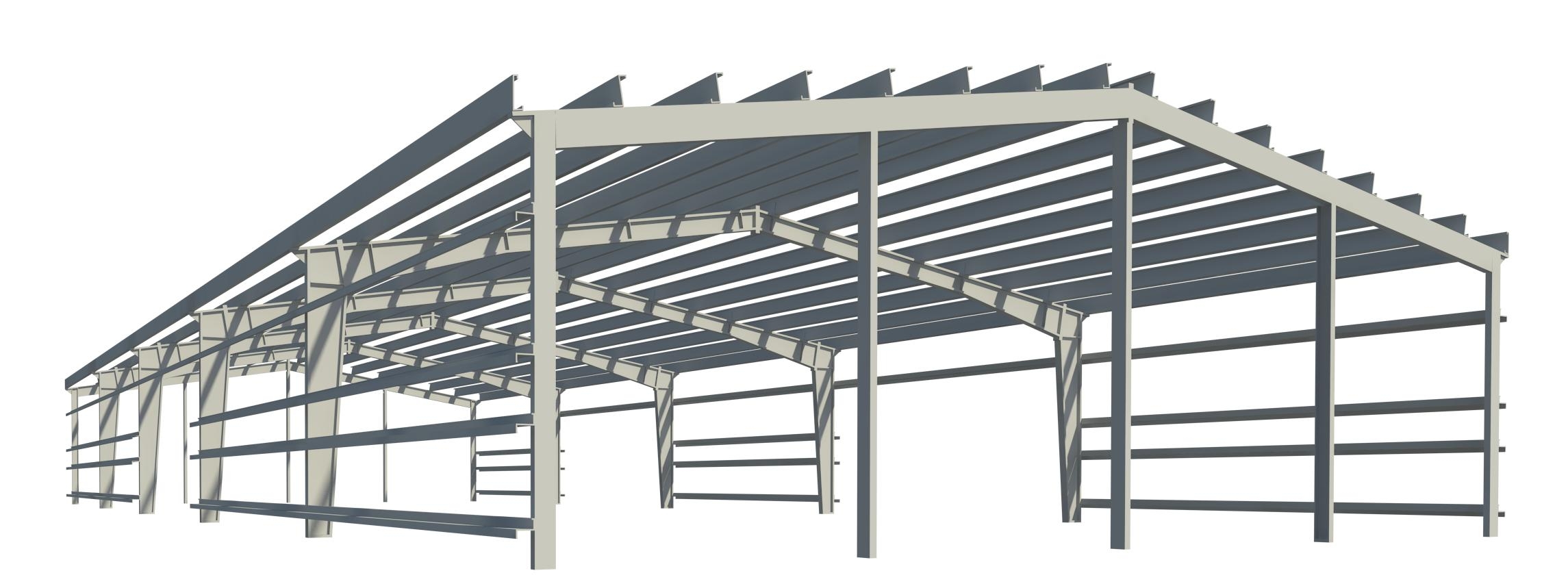
Pre-engineered steel buildings use a combination of built-up
sections, hot rolled sections and cold formed elements which provide the basic
steel frame work with a choice of single skin sheeting with added insulation or
insulated sandwich panels for roofing and wall cladding. The concept is
designed to provide a complete building envelope system which is airtight,
energy efficient, optimum in weight and cost and, above all, designed to fit
user requirement like a well fitted glove.
Pre engineered steel buildings can be fitted with different
structural accessories including mezzanine floors, canopies, fascias, interior
partitions etc. and the building is made water proof by use of special mastic
beads, filler strips and trims. This is very versatile buildings systems and
can be finished internally to serve any functions and accessorized externally
to achieve attractive and unique designing styles. It is very advantageous over
the conventional buildings and is really helpful in the low rise building
design.
Pre engineered buildings are generally low rise buildings
however the maximum eave height can go up to 25 to 30 meters. Low rise
buildings are ideal for offices, houses, showrooms, shop fronts etc. The
application of pre engineered buildings concept to low raise buildings is very
economical and speedy. Buildings can be constructed in less than half the
normal time especially when complemented with the other engineered sub systems.
The most common and economical type of low rise buildings is
a building with ground floor and two intermediate floor plus roof. The roof of
low rise buildings may be flat or sloped. Intermediate floors of low rise
buildings are made of mezzanine systems. Single storied houses for living take
minimum time for construction and can be built in any type of geographic
allocation like extreme cold hilly areas, high rain prone areas, plain land
obviously and extreme hot climatic zones as well.
Advantages:
Reduction in Construction Time: Buildings are typically
delivered in just a few weeks after approval of drawings. Foundation and anchor
bolts are cast parallel with finished, ready for the site bolting. In India the
use of PEB will reduce total construction time of the project by atleast 50%.
This also allows faster occupancy and earlier realization of revenue.
Lower Cost: Due
to the systems approach, there is a significant saving in design, manufacturing
and on site erection cost. The secondary members and cladding nest together
reducing transportation cost.
Flexibility
of Expansion: Buildings can be easily expanded in length by adding
additional bays. Also expansion in width and height is possible by pre
designing for future expansion. Larger Spans: Buildings can be supplied to
around 80M clear spans.
Quality
Control: As buildings are manufactured completely in the factory
under controlled conditions the quality is assured.
Low
Maintenance: Buildings are supplied with high quality paint systems
for cladding and steel to suit ambient conditions at the site, which results in
long durability and low maintenance costs.
Energy
Efficient Roofing and Wall Systems: Buildings can be supplied with
polyurethane insulated panels or fiberglass blankets insulation to achieve
required U values.
Architectural
Versatility: Building can be supplied with various types of fascias,
canopies, and curved eaves and are designed to receive pre cast concrete wall
panels, curtain walls, block walls and other wall systems.
Single
Source Availability: As the complete building package is supplied by
a single vendor, compatibility of all the building components and accessories
is assured. This is one of the major benefits of the pre engineered building
systems.
Benefits of
PEB:
Pre-engineered building systems provide real value to clients
without sacrificing durability, seismic and wind resistance, or aesthetic
appearance. Cost savings begin right at the drawing preparation stage. Systems
engineering and fabrication methods help reduce interim financing costs through
faster construction and minimized field erection expense. An added benefit is
earlier occupancy of the facility and a head start on day-to-day operations by
the client.
Apart from costs, there is an assurance of factory-built
quality and uniformity in design and fabrication. These systems are also energy
efficient; incorporate watertight roofing systems; enable easy disassembly or
future expansion and have the lowest life cycle maintenance costs. Adding to
these; there is no mess of sand and cement; power savings; walk able ceilings;
progressive and non-progressive panel systems for walls. A poor man can be
provided with a home created under strict quality control and having a longer
life span, with greater safety against natural disasters like earthquakes and
cyclones.
Moreover, it is possible to create the building in required
form and shape. And the ‘system approach’ renders a holistic way of thinking at
one platform for consultants, designers, architects, and builders. Thus it
tends to achieve a perfect harmony among various stringent specifications and
aesthetic requirements in a most economic way. In nutshell, the benefits may be
summarized as under
• Easy future expansion/modification.
• Weather proof and fire hazards.
• Optimized design of steel reducing
weight.
• International Quality Standards
• Seismic & Wind pressure resistant.
• Quality design, manufacturing and
erection, saving around 30-40% of project time
• Quick delivery and quick turn-key
construction.
• Pre-Painted and has low maintenance
requirement.
• Erection of the building is fast.
• The building can be dismantled and
relocated easily.
• Future extensions can be easily accommodated
without much hassle.
• Increased Life cycle performance and cost
competitiveness
• Environment friendly structures
• Better rainwater harvesting through
gutters and down-take arrangements
• Lighter weight; savings in foundation
cost of 10-20 percent
• The building can be dismantled and
relocated easily
• Easy integration of all construction
materials
• Energy efficient roof and wall system
using insulations.
• Suitability for Hilly regions and other
geographically difficult areas
• Unlimited architectural possibilities
Robin Thomas